Most people don't realise that there are several different types of vegetarian and many reasons why people become vegetarian. The definition of a vegetarian is someone who only eats fruits, vegetables, grains, cereals, nuts and seeds.
There are several types of vegetarian and they each have a different name. First there are the total vegetarians who eat only plant food, including fish eggs, dairy products or honey. Many vegetarians include some animal foods in their diet. Lacto-vegetarians will include a fe
"H"
this is about memories and this is about why people live.
Friday, October 22, 2010
Thursday, July 15, 2010
W A Mozart

Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (lahir di Salzburg, 27 Januari 1756 – meninggal di Wina, Austria, 5 Desember 1791 pada umur 35 tahun) adalah seorang komponis. Ia dianggap sebagai salah satu dari komponis musik klasik Eropa yang terpenting dan paling terkenal dalam sejarah. Karya-karyanya (sekitar 700 lagu) termasuk gubahan-gubahan yang secara luas diakui sebagai puncak karya musik simfoni, musik kamar, musik piano, musik opera, dan musik paduan suara. Contoh karyanya adalah opera Don Giovanni dan Die Zauberflöte. Banyak dari karya Mozart dianggap sebagai repertoar standar konser klasik dan diakui sebagai mahakarya musik zaman klasik. Karya-karyanya diurutkan dalam katalog Köchel-Verzeichnis.

Masa Awal (1756-1772)
Mozart, yang dikenal memiliki kemampuan tala mutlak (mengenal nada dengan tepat tanpa bantuan alat), mengenal musik sejak lahir. Ayahnya, Johann Georg Leopold Mozart adalah komponis penting pada jamannya, salah satu karyanya yang paling penting adalah Kindersinfonie ("Simfoni Anak-Anak"). Wolfgang adalah anak bungsu dari tujuh bersaudara yang meninggal prematur. Hanya dia dan Maria Anna Mozart ("Nannerl") yang bertahan hidup sampai dewasa. Sewaktu berumur empat tahun, Mozart sudah mampu memainkan harpsichord dan melakukan improvisasi pada karya-karya musik pendahulunya. Dia bahkan menulis komposisinya yang pertama saat berumur lima tahun. Karya-karyanya antara lain adalah Violin Sonata, dan beberapa Minuet. Leopold mengumpulkan semua komposisi ini tanpa sepengetahuan anaknya. Demikian halnya dengan Nannerl, dia juga adalah pemain keyboard yang sangat handal. Leopold yang menemukan bakat kedua anaknya merasa “terpanggil” untuk memamerkan mereka ke seluruh Eropa.

Bermain piano di depan Raja Bayern
Mozart kemudian dibawa untuk bermain piano di depan raja Bayern di München. Pada bulan September 1762, Leopold mengambil cuti panjang dari jabatannya untuk mempromosikan anaknya kepada raja-raja. Mereka lalu berangkat ke Wina. Di sana Mozart bermain piano di depan Ratu Maria Theresia yang terpukau akan keahlian permainan Mozart dan Nannerl. Setelah konser ini, Mozart harus mengikuti konser yang cukup panjang selama tiga tahun yaitu Paris (1763, 1765) dan London (1764-1765). Di tempat-tempat tersebut, Mozart mengadakan konser di depan raja-raja dan juga diuji oleh mereka. Antara lain dengan mengimprovisasi tema-tema yang diberikan oleh penguji dengan mata yang ditutup selembar kain. Mozart disambut sebagai anak ajaib di segala tempat. Di London, dia juga bertemu dengan anak dari Johann Sebastian Bach, yaitu Johann Christian Bach yang sering dipanggil sebagai English Bach. Mozart memainkan piano sonata dalam empat tangan sembari duduk di pangkuan Bach.
Simfoni-simfoni dari Bach dan Carl Friedrich Abel mempengaruhi simfoni-simfoni Mozart yang pertama (K.16 & K.19), yang pada tahun 1764 & 1765. Pada 1767, Mozart menggubah beberapa piano sonata dari komponis-komonis lain dan membuatnya menjadi empat buah piano Concerto pertamanya (K.37, K.39, K.40, K.41). Pada tahun 1768, atas permintaan Kaisar Wina, Mozart menggubah Opera buffa (komik opera), La Finta Semplice (namun tak terpentaskan) dan operetta Bastien und Bastienne.

Perjalanan ke Italia
Pada tahun 1769, Mozart mengadakan perjalanan ke Italia. Hasil perjalanan ini cukup baik, Mozart sangat produktif dalam penciptaan komposisi. Dia menggubah opera Mitridati, rè di Ponto (1770) dan Lucia Silla (1772) dan keduanya mendapat sukses besar dalam pertunjukannya di Milano. Mozart juga mencipatakan banyak simfoni selama perjalanan ini, dan dipengaruhi para komponis-komponis italia seperti Sammartini. Di Bologna, Mozart juga mempelajari Kontrapung pada guru komposisi yang paling terkenal pada masa itu, Padre Martini.

Masa terakhir (1784-1791)
Puncak karier Mozart terdapat di masa 1784-1786. Mozart sangat rajin menggubah. Dia membuat duabelas Concerto dan dianggap para musikolog sebagai karyanya yang paling penting. Walau Kaisar Joseph II ikut mendengar konser Mozart, hal itu sama sekali tak membantu keuangannya. Mozart diberi jabatan sebagai pemusik istana dengan gaji yang tak terlalu besar.
Tuesday, June 1, 2010
Produk-produk Pasar Modal
Pasar modal di Indonesia semakin hari tentunya semakin meningkat pelaku pasar modal dan nilai perdagangannya. Hal ini harus diimbangi oleh pengetahuan yang baik bagi siapa saja yang ingin “bermain” di pasar modal, minimal mengetahui apa saja produk yang dihasilkan pasar modal.
Instrumen atau produk yang diperdagangkan di Pasar Modal disebut dengan Efek. Efek adalah surat berharga, yaitu surat pengakuan utang, surat berharga komersial, saham, obligasi, tanda bukti utang, Unit Penyertaan kontrak investasi kolektif, kontrak berjangka atas Efek, dan setiap derivatif dari Efek. Berikut adalah produk-produk pasar modal :
1. Saham (Stocks)
Saham pada dasarnya adalah bukti pemilikan atas suatu perusahaan berbentuk Perseroan Terbatas (PT). Saham terbagi atas dua jenis, yaitu :
a. Saham Biasa (Common Stocks)
Di antara surat-surat berharga yang diperdagangkan di pasar modal, saham biasa (common stock) adalah yang paling dikenal masyarakat. Di antara emiten (perusahaan yang menerbitkan surat berharga), saham biasa juga merupakan yang paling banyak digunakan untuk menarik dana dari masyarakat. Jadi saham biasa paling menarik, baik bagi pemodal maupun bagi emiten. Apakah Saham itu? Secara sederhana, saham dapat didefinisikan sebagai tanda penyertaan atau pemilikan seseorang atau badan dalam suatu perusahaan. Wujud saham adalah, selembar kertas yang menerangkan bahwa pemilik kertas tersebut adalah pemilik perusahaan yang menerbitkan kertas tersebut. Jadi sama dengan menabung di bank. Setiap kali kita menabung, maka kita akan mendapat slip yang menjelaskan bahwa kita telah menyetor sejumlah uang. Bila kita membeli saham, maka kita akan menerima kertas yang menjelaskan bahwa kita memiliki perusahaan penerbit saham tersebut.
b. Saham Preferen (Preferred Stocks)
Saham Preferen merupakan saham yang memiliki karakteristik gabungan antara obligasi dan saham biasa, karena bisa menghasilkan pendapatan tetap (seperti bunga obligasi), tetapi juga bisa tidak mendatangkan hasil seperti yang dikehendaki investor. Saham preferen serupa dengan saham biasa karena dua hal, yaitu: mewakili kepemilikan ekuitas dan diterbitkan tanpa tanggal jatuh tempo yang tertulis di atas lembaran saham tersebut; dan membayar dividen. Sedangkan persamaan antara saham preferen dengan obligasi terletak pada tiga hal: ada klaim atas laba dan aktiva sebelumnya; dividennya tetap selama masa berlaku (hidup) dari saham; memiliki hak tebus dan dapat dipertukarkan (convertible) dengan saham biasa. Oleh karena saham preferen diperdagangkan berdasarkan hasil yang ditawarkan kepada investor, maka secara praktis saham preferen dipandang sebagai surat berharga dengan pendapatan tetap dan karena itu akan bersaing dengan obligasi di pasar. Walaupun demikian, obligasi perusahaan menduduki tempat yang lebih senior dibanding dengan saham preferen.
2. Obligasi (Bond)
Obligasi adalah surat berharga atau sertifikat yang berisi kontrak antara pemberi dana (dalam hal ini pemodal) dengan yang diberi dana (emiten). Jadi surat obligasi adalah selembar kertas yang menyatakan bahwa pemilik kertas tersebut telah membeli hutang perusahaan yang menerbitkan obligasi. Penerbit membayar bunga atas obligasi tersebut pada tanggal-tanggal yg telah ditentukan secara periodik, dan pada akhirnya menebus nilai utang tersebut pada saat jatuh tempo dengan mengembalikan jumlah pokok pinjaman ditambah bunga yg terutang. Pada umumnya, instrumen ini memberikan bunga yang tetap secara periodik. Bila bunga dalam sistem ekonomi menurun, nilai obligasi naik; dan sebaliknya jika bunga meningkat, nilai obligasi turun.
3. Obligasi Konversi (Convertible Bond)
Obligasi konversi, sekilas tidak ada bedanya dengan obligasi biasa, misalnya, memberikan kupon yang tetap, memiliki waktu jatuh tempo dan memiliki nilai “face value”. Hanya saja, obligasi konversi memiliki keunikan, yaitu bisa ditukar dengan saham biasa. Pada obligasi konversi selalu tercantum persyaratan untuk melakukan konversi. Misalnya, setiap obligasi konversi bisa dikonversi menjadi 3 lembar saham biasa setelah 1 Januari 2006. Persyaratan ini tidak sama diantara obligasi konversi yang satu dengan yang lainnya. Obligasi konversi (convertible bond), sudah dikenal di pasar modal Indonesia. Untuk kalangan emiten swasta, sebenarnya obligasi konversi lebih dulu populer daripada obligasi. Kecenderungan melakukan emisi obligasi baru menunjukkan aktivitas yang meningkat sejak tahun 1992, sedang obligasi konversi sudah memasuki pasar menjelang akhir tahun 1990.
4. Reksa Dana (Mutual Funds)
Reksa dana merupakan salah satu alternatif investasi bagi masyarakat pemodal, khususnya pemodal kecil dan pemodal yang tidak memiliki banyak waktu dan keahlian untuk menghitung risiko atas investasi mereka. Reksa Dana dirancang sebagai sarana untuk menghimpun dana dari masyarakat yang memiliki modal, mempunyai keinginan untuk melakukan investasi, namun hanya memiliki waktu dan pengetahuan yang terbatas. Selain itu Reksa Dana juga diharapkan dapat meningkatkan peran pemodal lokal untuk berinvestasi di pasar modal Indonesia. Dilihat dari asal kata-nya, Reksa Dana berasal dari kosa kata “reksa” yang berarti jaga atau pelihara dan kata “dana” yang berarti kumpulan uang, sehingga reksa dana dapat diartikan sebagai “kumpulan uang yang dipelihara bersama untuk suatu kepentingan”. Umumnya, Reksa Dana diartikan sebagai wadah yang dipergunakan untuk menghimpun dana dari masyarakat pemodal untuk selanjutnya diinvestasikan dalam portofolio Efek oleh Manajer Investasi.
Instrumen atau produk yang diperdagangkan di Pasar Modal disebut dengan Efek. Efek adalah surat berharga, yaitu surat pengakuan utang, surat berharga komersial, saham, obligasi, tanda bukti utang, Unit Penyertaan kontrak investasi kolektif, kontrak berjangka atas Efek, dan setiap derivatif dari Efek. Berikut adalah produk-produk pasar modal :
1. Saham (Stocks)
Saham pada dasarnya adalah bukti pemilikan atas suatu perusahaan berbentuk Perseroan Terbatas (PT). Saham terbagi atas dua jenis, yaitu :
a. Saham Biasa (Common Stocks)
Di antara surat-surat berharga yang diperdagangkan di pasar modal, saham biasa (common stock) adalah yang paling dikenal masyarakat. Di antara emiten (perusahaan yang menerbitkan surat berharga), saham biasa juga merupakan yang paling banyak digunakan untuk menarik dana dari masyarakat. Jadi saham biasa paling menarik, baik bagi pemodal maupun bagi emiten. Apakah Saham itu? Secara sederhana, saham dapat didefinisikan sebagai tanda penyertaan atau pemilikan seseorang atau badan dalam suatu perusahaan. Wujud saham adalah, selembar kertas yang menerangkan bahwa pemilik kertas tersebut adalah pemilik perusahaan yang menerbitkan kertas tersebut. Jadi sama dengan menabung di bank. Setiap kali kita menabung, maka kita akan mendapat slip yang menjelaskan bahwa kita telah menyetor sejumlah uang. Bila kita membeli saham, maka kita akan menerima kertas yang menjelaskan bahwa kita memiliki perusahaan penerbit saham tersebut.
b. Saham Preferen (Preferred Stocks)
Saham Preferen merupakan saham yang memiliki karakteristik gabungan antara obligasi dan saham biasa, karena bisa menghasilkan pendapatan tetap (seperti bunga obligasi), tetapi juga bisa tidak mendatangkan hasil seperti yang dikehendaki investor. Saham preferen serupa dengan saham biasa karena dua hal, yaitu: mewakili kepemilikan ekuitas dan diterbitkan tanpa tanggal jatuh tempo yang tertulis di atas lembaran saham tersebut; dan membayar dividen. Sedangkan persamaan antara saham preferen dengan obligasi terletak pada tiga hal: ada klaim atas laba dan aktiva sebelumnya; dividennya tetap selama masa berlaku (hidup) dari saham; memiliki hak tebus dan dapat dipertukarkan (convertible) dengan saham biasa. Oleh karena saham preferen diperdagangkan berdasarkan hasil yang ditawarkan kepada investor, maka secara praktis saham preferen dipandang sebagai surat berharga dengan pendapatan tetap dan karena itu akan bersaing dengan obligasi di pasar. Walaupun demikian, obligasi perusahaan menduduki tempat yang lebih senior dibanding dengan saham preferen.
2. Obligasi (Bond)
Obligasi adalah surat berharga atau sertifikat yang berisi kontrak antara pemberi dana (dalam hal ini pemodal) dengan yang diberi dana (emiten). Jadi surat obligasi adalah selembar kertas yang menyatakan bahwa pemilik kertas tersebut telah membeli hutang perusahaan yang menerbitkan obligasi. Penerbit membayar bunga atas obligasi tersebut pada tanggal-tanggal yg telah ditentukan secara periodik, dan pada akhirnya menebus nilai utang tersebut pada saat jatuh tempo dengan mengembalikan jumlah pokok pinjaman ditambah bunga yg terutang. Pada umumnya, instrumen ini memberikan bunga yang tetap secara periodik. Bila bunga dalam sistem ekonomi menurun, nilai obligasi naik; dan sebaliknya jika bunga meningkat, nilai obligasi turun.
3. Obligasi Konversi (Convertible Bond)
Obligasi konversi, sekilas tidak ada bedanya dengan obligasi biasa, misalnya, memberikan kupon yang tetap, memiliki waktu jatuh tempo dan memiliki nilai “face value”. Hanya saja, obligasi konversi memiliki keunikan, yaitu bisa ditukar dengan saham biasa. Pada obligasi konversi selalu tercantum persyaratan untuk melakukan konversi. Misalnya, setiap obligasi konversi bisa dikonversi menjadi 3 lembar saham biasa setelah 1 Januari 2006. Persyaratan ini tidak sama diantara obligasi konversi yang satu dengan yang lainnya. Obligasi konversi (convertible bond), sudah dikenal di pasar modal Indonesia. Untuk kalangan emiten swasta, sebenarnya obligasi konversi lebih dulu populer daripada obligasi. Kecenderungan melakukan emisi obligasi baru menunjukkan aktivitas yang meningkat sejak tahun 1992, sedang obligasi konversi sudah memasuki pasar menjelang akhir tahun 1990.
4. Reksa Dana (Mutual Funds)
Reksa dana merupakan salah satu alternatif investasi bagi masyarakat pemodal, khususnya pemodal kecil dan pemodal yang tidak memiliki banyak waktu dan keahlian untuk menghitung risiko atas investasi mereka. Reksa Dana dirancang sebagai sarana untuk menghimpun dana dari masyarakat yang memiliki modal, mempunyai keinginan untuk melakukan investasi, namun hanya memiliki waktu dan pengetahuan yang terbatas. Selain itu Reksa Dana juga diharapkan dapat meningkatkan peran pemodal lokal untuk berinvestasi di pasar modal Indonesia. Dilihat dari asal kata-nya, Reksa Dana berasal dari kosa kata “reksa” yang berarti jaga atau pelihara dan kata “dana” yang berarti kumpulan uang, sehingga reksa dana dapat diartikan sebagai “kumpulan uang yang dipelihara bersama untuk suatu kepentingan”. Umumnya, Reksa Dana diartikan sebagai wadah yang dipergunakan untuk menghimpun dana dari masyarakat pemodal untuk selanjutnya diinvestasikan dalam portofolio Efek oleh Manajer Investasi.
Monday, April 19, 2010
Geography

Geography (from Greek γεωγραφία - geographia, lit. "earth describe)is the study of the Earth and its lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena. A literal translation would be "to describe or write about the Earth". The first person to use the word "geography" was Eratosthenes (276-194 B.C.). Four historical traditions in geographical research are the spatial analysis of natural and human phenomena (geography as a study of distribution), area studies (places and regions), study of man-land relationship, and research in earth sciences. Nonetheless, modern geography is an all-encompassing discipline that foremost seeks to understand the Earth and all of its human and natural complexities—not merely where objects are, but how they have changed and come to be. As "the bridge between the human and physical sciences," geography is divided into two main branches—human geography and physical geography.
Traditionally, geographers have been viewed the same way as cartographers and people who study place names and numbers. Although many geographers are trained in toponymy and cartology, this is not their main preoccupation. Geographers study the spatial and temporal distribution of phenomena, processes and features as well as the interaction of humans and their environment. As space and place affect a variety of topics such as economics, health, climate, plants and animals, geography is highly interdisciplinary.
Geography as a discipline can be split broadly into two main subsidiary fields: human geography and physical geography. The former focuses largely on the built environment and how space is created, viewed and managed by humans as well as the influence humans have on the space they occupy. The latter examines the natural environment and how the climate, vegetation & life, soil, water, and landforms are produced and interact. As a result of the two subfields using different approaches a third field has emerged, which is environmental geography. Environmental geography combines physical and human geography and looks at the interactions between the environment and humans.
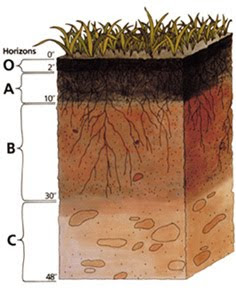
Soil is not only a support for vegetation, but it is also the zone (the pedosphere) of numerous interactions between climate (water, air, temperature), soil life (micro-organisms, plants, animals) and its residues, the mineral material of the original and added rock, and its position in the landscape. During its formation and genesis, the soil profile slowly deepens and develops characteristic layers, called 'horizons', while a steady state balance is approached.
Soil users (such as agronomists) showed initially little concern in the dynamics of soil. They saw it as medium whose chemical, physical and biological properties were useful for the services of agronomic productivity . On the other hand, pedologists and geologists did not initially focus on the agronomic applications of the soil characteristics (edaphic properties) but upon its relation to the nature and history of landscapes. Today, there's an integration of the two disciplinary approaches as part of landscape and environmental sciences.
Pedologists are now also interested in the practical applications of a good understanding of pedogenesis processes (the evolution and functioning of soils), like interpreting its environmental history and predicting consequences of changes in land use, while agronomists understand that the cultivated soil is a complex medium, often resulting from several thousands of years of evolution. They understand that the current balance is fragile and that only a thorough knowledge of its history makes it possible to ensure its sustainable use.
Hydrology is the study of the movement, distribution, and quality of water throughout Earth, and thus addresses both the hydrologic cycle and water resources. A practitioner of hydrology is a hydrologist, working within the fields of either earth or environmental science, physical geography, geology or civil and environmental engineering.
Domains of hydrology include hydrometeorology, surface hydrology, hydrogeology, drainage basin management and water chemistry, where water plays the central role. Oceanography and meteorology are not included because water is only one of many important aspects.
Hydrological research is useful as it allows us to better understand the world in which we live, and also provides insight for environmental engineering, policy and planning.
Hydrogeology (hydro- meaning water, and -geology meaning the study of the Earth) is the area of geology that deals with the distribution and movement of groundwater in the soil and rocks of the Earth's crust, (commonly in aquifers). The term geohydrology is often used interchangeably. Some make the minor distinction between a hydrologist or engineer applying themselves to geology (geohydrology), and a geologist applying themselves to hydrology (hydrogeology).
Friday, April 2, 2010
Family Planning
Family planning is the planning of when to have children, and the use of birth control and other techniques to implement such plans. Other techniques commonly used include sexuality education, prevention and management of sexually transmitted infections, pre-conception counseling and management, and infertility management.
Family planning is sometimes used as a synonym for the use of birth control, though it often includes more. It is most usually applied to a female-male couple who wish to limit the number of children they have and/or to control the timing of pregnancy (also known as spacing children).
Family planning services are defined as "educational, comprehensive medical or social activities which enable individuals, including minors, to determine freely the number and spacing of their children and to select the means by which this may be achieved."
Raising a child requires significant amounts of resources: time, social, financial, environmental. Planning can help assure that resources are available.
Waiting until the mother is at least 18 years old before trying to have children improves maternal and child health. Also, if additional children are desired after a child is born, it is healthier for the mother and the child to wait at least 2 years after the previous birth before attempting to conceive (but not more than 5 years). After a miscarriage or abortion, it is healthier to wait at least 6 months.
Childbirth and prenatal health care cost averaged $7,090 for normal delivery in the US in 1996. US Department of Agriculture estimates that for a child born in 2007, a US family will spend an average of $11,000 to $23,000 per year for the first 17 years of child's life. (Total inflation adjusted estimated expenditure: $196,000 to $393,000, depending on household income.)
The world's largest international source of funding for population and reproductive health programs is the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA). The main goals of the International Conference on Population and Development Program of Action are:
* Universal access to reproductive health services by 2015
* Universal primary education and closing the gender gap in education by 2015
* Reducing maternal mortality by 75% by 2015
* Reducing infant mortality
* Increasing life expectancy
* Reducing HIV infection rates in persons aged 15–24 years by 25% in the most-affected countries by 2005, and by 25% globally by 2010
The World health organization (WHO) and World Bank estimate that $3.00 per person per year would provide basic family planning, maternal and neonatal health care to women in developing countries. This would include contraception, prenatal, delivery and post-natal care in addition to postpartum family planning and the promotion of condoms to prevent sexually transmitted infections.[9]
China's one-child policy encourages couples to have no more than one child. China's population policy has been credited with a very significant slowing of China's population growth which had been very high before the policy was implemented. It has come under criticism that the implementation of the policy has involved forced abortions and forced sterilization. However, while the punishment of "unplanned" pregnancy is a fine, both forced abortion and forced sterilization can be charged with intentional assault, which is punished with up to 10 years' imprisonment.
*In Hong Kong, the Two is Enough campaign in 1970s encouraged people to have 2 or less children in each family, it contributed to the reduced birth rate in the following decades.*
In Hong Kong, the Eugenics League was found in 1936, which became The Family Planning Association of Hong Kong in 1950. The organisation provides family planning advice, sex education, birth control services to the general public of Hong Kong. In the 1970's, due to the rapidly rising population, it launched the "Two is Enough" campaign, which reduced the general birth rate through educational means.
The Family Planning Association of Hong Kong, Hong Kong's national family planning association, founded the International Planned Parenthood Federation with its counterparts in seven other countries.
Iran is another country which has succeeded in sharply reducing its birth rate in recent years.
Title X of the Public Health Service Act, is a US government program dedicated to providing family planning services for those in need. But funding for Title X as a percentage of total public funding to family planning client services has steadily declined from 44% of total expenditures in 1980 to 12% in 2006. Medicaid has increased from 20% to 71% in the same time. In 2006, Medicaid contributed $1.3 billion to public family planning.
The Indian government has come up with measures to control population and increase awareness of the benefits of reducing population growth, which include better lifestyle, education, environment, health and well being of every individual. Despite these attempts, couples[who?] cite the need for company for their child.[citation needed] Couples[who?] feel that they can afford more than one child. Awareness campaigns include "We two, our's one", "Girl or Boy, let there just be one child".[citation needed] There is also still the mistrust of family planning policies due to the forced sterilizations that took place during The Emergency.
Family planning is sometimes used as a synonym for the use of birth control, though it often includes more. It is most usually applied to a female-male couple who wish to limit the number of children they have and/or to control the timing of pregnancy (also known as spacing children).
Family planning services are defined as "educational, comprehensive medical or social activities which enable individuals, including minors, to determine freely the number and spacing of their children and to select the means by which this may be achieved."
Raising a child requires significant amounts of resources: time, social, financial, environmental. Planning can help assure that resources are available.
Waiting until the mother is at least 18 years old before trying to have children improves maternal and child health. Also, if additional children are desired after a child is born, it is healthier for the mother and the child to wait at least 2 years after the previous birth before attempting to conceive (but not more than 5 years). After a miscarriage or abortion, it is healthier to wait at least 6 months.
Childbirth and prenatal health care cost averaged $7,090 for normal delivery in the US in 1996. US Department of Agriculture estimates that for a child born in 2007, a US family will spend an average of $11,000 to $23,000 per year for the first 17 years of child's life. (Total inflation adjusted estimated expenditure: $196,000 to $393,000, depending on household income.)
The world's largest international source of funding for population and reproductive health programs is the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA). The main goals of the International Conference on Population and Development Program of Action are:
* Universal access to reproductive health services by 2015
* Universal primary education and closing the gender gap in education by 2015
* Reducing maternal mortality by 75% by 2015
* Reducing infant mortality
* Increasing life expectancy
* Reducing HIV infection rates in persons aged 15–24 years by 25% in the most-affected countries by 2005, and by 25% globally by 2010
The World health organization (WHO) and World Bank estimate that $3.00 per person per year would provide basic family planning, maternal and neonatal health care to women in developing countries. This would include contraception, prenatal, delivery and post-natal care in addition to postpartum family planning and the promotion of condoms to prevent sexually transmitted infections.[9]
China's one-child policy encourages couples to have no more than one child. China's population policy has been credited with a very significant slowing of China's population growth which had been very high before the policy was implemented. It has come under criticism that the implementation of the policy has involved forced abortions and forced sterilization. However, while the punishment of "unplanned" pregnancy is a fine, both forced abortion and forced sterilization can be charged with intentional assault, which is punished with up to 10 years' imprisonment.
*In Hong Kong, the Two is Enough campaign in 1970s encouraged people to have 2 or less children in each family, it contributed to the reduced birth rate in the following decades.*
In Hong Kong, the Eugenics League was found in 1936, which became The Family Planning Association of Hong Kong in 1950. The organisation provides family planning advice, sex education, birth control services to the general public of Hong Kong. In the 1970's, due to the rapidly rising population, it launched the "Two is Enough" campaign, which reduced the general birth rate through educational means.
The Family Planning Association of Hong Kong, Hong Kong's national family planning association, founded the International Planned Parenthood Federation with its counterparts in seven other countries.
Iran is another country which has succeeded in sharply reducing its birth rate in recent years.
Title X of the Public Health Service Act, is a US government program dedicated to providing family planning services for those in need. But funding for Title X as a percentage of total public funding to family planning client services has steadily declined from 44% of total expenditures in 1980 to 12% in 2006. Medicaid has increased from 20% to 71% in the same time. In 2006, Medicaid contributed $1.3 billion to public family planning.
The Indian government has come up with measures to control population and increase awareness of the benefits of reducing population growth, which include better lifestyle, education, environment, health and well being of every individual. Despite these attempts, couples[who?] cite the need for company for their child.[citation needed] Couples[who?] feel that they can afford more than one child. Awareness campaigns include "We two, our's one", "Girl or Boy, let there just be one child".[citation needed] There is also still the mistrust of family planning policies due to the forced sterilizations that took place during The Emergency.
Population Growth
Population growth is the change in a population over time, and can be quantified as the change in the number of individuals of any species in a population using "per unit time" for measurement. In biology, the term population growth is likely to refer to any known organism, but this article deals mostly with the application of the term to human populations in demography.
In demography, population growth is used informally for the more specific term population growth rate (see below), and is often used to refer specifically to the growth of the human population of the world.
Estimated size of human population from 10,000 BCE–2000 CE.
Population growth is the change in a population over time, and can be quantified as the change in the number of
In demographics and ecology, Population growth rate (PGR) is the fractional rate at which the number of individuals in a population increases. Specifically, PGR ordinarily refers to the change in population over a unit time period, often expressed as a percentage of the number of individuals in the population at the beginning of that period. This can be written as the formula:
\mathrm{Growth\ rate} = \frac{(\mathrm{population\ at\ end\ of\ period}\ -\ \mathrm{population\ at\ beginning\ of\ period})} {\mathrm{population\ at\ beginning\ of\ period}}
(In the limit of a sufficiently small time period.)
The above formula can be expanded to: growth rate = crude birth rate - crude death rate + net immigration rate, or ∆P/P = (B/P) - (D/P) + (I/P) - (E/P), where P is the total population, B is the number of births, D is the number of deaths, I is the number of immigrants, and E is the number of emigrants.
This formula allows for the identification of the source of population growth, whether due to natural increase or an increase in the net immigration rate. Natural increase is an increase in the native-born population, stemming from either a higher birth rate, a lower death rate, or a combination of the two. Net immigration rate is the difference between the number of immigrants and the number of emigrants.
The most common way to express population growth is as a ratio, not as a rate. The change in population over a unit time period is expressed as a percentage of the population at the beginning of the time period. That is:
\mathrm{Growth\ ratio} = \mathrm{Growth\ rate} \times 100%.
A positive growth ratio (or rate) indicates that the population is increasing, while a negative growth ratio indicates the population is decreasing. A growth ratio of zero indicates that there were the same number of people at the two times -- net difference between births, deaths and migration is zero. However, a growth rate may be zero even when there are significant changes in the birth rates, death rates, immigration rates, and age distribution between the two times. [1] Equivalently, percent death rate = the average number of deaths in a year for every 100 people in the total population.
A related measure is the net reproduction rate. In the absence of migration, a net reproduction rate of more than one indicates that the population of women is increasing, while a net reproduction rate less than one (sub-replacement fertility) indicates that the population of women is decreasing.
[edit] Human population growth rate
Annual population growth rate in percent, as listed in the CIA World Factbook (2006 estimate).[2]
Growth rate of world population (1950-2000)
Population of the world from 10,000 BCE to 2000 CE (logarithmic scale)
In demography, population growth is used informally for the more specific term population growth rate (see below), and is often used to refer specifically to the growth of the human population of the world.
Estimated size of human population from 10,000 BCE–2000 CE.
Population growth is the change in a population over time, and can be quantified as the change in the number of
In demographics and ecology, Population growth rate (PGR) is the fractional rate at which the number of individuals in a population increases. Specifically, PGR ordinarily refers to the change in population over a unit time period, often expressed as a percentage of the number of individuals in the population at the beginning of that period. This can be written as the formula:
\mathrm{Growth\ rate} = \frac{(\mathrm{population\ at\ end\ of\ period}\ -\ \mathrm{population\ at\ beginning\ of\ period})} {\mathrm{population\ at\ beginning\ of\ period}}
(In the limit of a sufficiently small time period.)
The above formula can be expanded to: growth rate = crude birth rate - crude death rate + net immigration rate, or ∆P/P = (B/P) - (D/P) + (I/P) - (E/P), where P is the total population, B is the number of births, D is the number of deaths, I is the number of immigrants, and E is the number of emigrants.
This formula allows for the identification of the source of population growth, whether due to natural increase or an increase in the net immigration rate. Natural increase is an increase in the native-born population, stemming from either a higher birth rate, a lower death rate, or a combination of the two. Net immigration rate is the difference between the number of immigrants and the number of emigrants.
The most common way to express population growth is as a ratio, not as a rate. The change in population over a unit time period is expressed as a percentage of the population at the beginning of the time period. That is:
\mathrm{Growth\ ratio} = \mathrm{Growth\ rate} \times 100%.
A positive growth ratio (or rate) indicates that the population is increasing, while a negative growth ratio indicates the population is decreasing. A growth ratio of zero indicates that there were the same number of people at the two times -- net difference between births, deaths and migration is zero. However, a growth rate may be zero even when there are significant changes in the birth rates, death rates, immigration rates, and age distribution between the two times. [1] Equivalently, percent death rate = the average number of deaths in a year for every 100 people in the total population.
A related measure is the net reproduction rate. In the absence of migration, a net reproduction rate of more than one indicates that the population of women is increasing, while a net reproduction rate less than one (sub-replacement fertility) indicates that the population of women is decreasing.
[edit] Human population growth rate
Annual population growth rate in percent, as listed in the CIA World Factbook (2006 estimate).[2]
Growth rate of world population (1950-2000)
Population of the world from 10,000 BCE to 2000 CE (logarithmic scale)
Friday, March 19, 2010
Business Plan
A business plan is a formal statement of a set of business goals, the reasons why they are believed attainable, and the plan for reaching those goals. It may also contain background information about the organization or team attempting to reach those goals.
The business goals may be defined for for-profit or for non-profit organizations. For-profit business plans typically focus on financial goals, such as profit or creation of wealth. Non-profit and government agency business plans tend to focus on organizational mission which is the basis for their governmental status or their non-profit, tax-exempt status, respectively—although non-profits may also focus on optimizing revenue. In non-profit organizations, creative tensions may develop in the effort to balance mission with "margin" (or revenue). Business plans may also target changes in perception and branding by the customer, client, tax-payer, or larger community. A business plan having changes in perception and branding as its primary goals is called a marketing plan.
Business plans may be internally or externally focused. Externally focused plans target goals that are important to external stakeholders, particularly financial stakeholders. They typically have detailed information about the organization or team attempting to reach the goals. With for-profit entities, external stakeholders include investors and customers. External stake-holders of non-profits include donors and the clients of the non-profit's services. For government agencies, external stakeholders include tax-payers, higher-level government agencies, and international lending bodies such as the IMF, the World Bank, various economic agencies of the UN, and development banks.
Internally focused business plans target intermediate goals required to reach the external goals. They may cover the development of a new product, a new service, a new IT system, a restructuring of finance, the refurbishing of a factory or a restructuring of the organization. An internal business plan is often developed in conjunction with a balanced scorecard or a list of critical success factors. This allows success of the plan to be measured using non-financial measures. Business plans that identify and target internal goals, but provide only general guidance on how they will be met are called strategic plans.
Operational plans describe the goals of an internal organization, working group or department. Project plans, sometimes known as project frameworks, describe the goals of a particular project. They may also address the project's place within the organization's larger strategic goals.
Business plans are decision-making tools. There is no fixed content for a business plan. Rather the content and format of the business plan is determined by the goals and audience. A business plan should contain whatever information is needed to decide whether or not to pursue a goal.
For example, a business plan for a non-profit might discuss the fit between the business plan and the organization’s mission. Banks are quite concerned about defaults, so a business plan for a bank loan will build a convincing case for the organization’s ability to repay the loan. Venture capitalists are primarily concerned about initial investment, feasibility, and exit valuation. A business plan for a project requiring equity financing will need to explain why current resources, upcoming growth opportunities, and sustainable competitive advantage will lead to a high exit valuation.
Preparing a business plan draws on a wide range of knowledge from many different business disciplines: finance, human resource management, intellectual property management, supply chain management, operations management, and marketing, among others. It can be helpful to view the business plan as a collection of sub-plans, one for each of the main business disciplines.
"... a good business plan can help to make a good business credible, understandable, and attractive to someone who is unfamiliar with the business. Writing a good business plan can’t guarantee success, but it can go a long way toward reducing the odds of failure."
Traditionally business plans have been highly confidential and quite limited in audience. The business plan itself is generally regarded as secret. However the emergence of free software and open source has opened the model and made the notion of an open business plan possible.
An open business plan is a business plan with unlimited audience. The business plan is typically web published and made available to all.
In the free software and open source business model, trade secrets, copyright and patents can no longer be used as effective locking mechanisms to provide sustainable advantages to a particular business and therefore a secret business plan is less relevant in those models.
While the origin of the open business plan model is in the free software and Libre services arena, the concept is likely applicable to other domains.
The business goals may be defined for for-profit or for non-profit organizations. For-profit business plans typically focus on financial goals, such as profit or creation of wealth. Non-profit and government agency business plans tend to focus on organizational mission which is the basis for their governmental status or their non-profit, tax-exempt status, respectively—although non-profits may also focus on optimizing revenue. In non-profit organizations, creative tensions may develop in the effort to balance mission with "margin" (or revenue). Business plans may also target changes in perception and branding by the customer, client, tax-payer, or larger community. A business plan having changes in perception and branding as its primary goals is called a marketing plan.
Business plans may be internally or externally focused. Externally focused plans target goals that are important to external stakeholders, particularly financial stakeholders. They typically have detailed information about the organization or team attempting to reach the goals. With for-profit entities, external stakeholders include investors and customers. External stake-holders of non-profits include donors and the clients of the non-profit's services. For government agencies, external stakeholders include tax-payers, higher-level government agencies, and international lending bodies such as the IMF, the World Bank, various economic agencies of the UN, and development banks.
Internally focused business plans target intermediate goals required to reach the external goals. They may cover the development of a new product, a new service, a new IT system, a restructuring of finance, the refurbishing of a factory or a restructuring of the organization. An internal business plan is often developed in conjunction with a balanced scorecard or a list of critical success factors. This allows success of the plan to be measured using non-financial measures. Business plans that identify and target internal goals, but provide only general guidance on how they will be met are called strategic plans.
Operational plans describe the goals of an internal organization, working group or department. Project plans, sometimes known as project frameworks, describe the goals of a particular project. They may also address the project's place within the organization's larger strategic goals.
Business plans are decision-making tools. There is no fixed content for a business plan. Rather the content and format of the business plan is determined by the goals and audience. A business plan should contain whatever information is needed to decide whether or not to pursue a goal.
For example, a business plan for a non-profit might discuss the fit between the business plan and the organization’s mission. Banks are quite concerned about defaults, so a business plan for a bank loan will build a convincing case for the organization’s ability to repay the loan. Venture capitalists are primarily concerned about initial investment, feasibility, and exit valuation. A business plan for a project requiring equity financing will need to explain why current resources, upcoming growth opportunities, and sustainable competitive advantage will lead to a high exit valuation.
Preparing a business plan draws on a wide range of knowledge from many different business disciplines: finance, human resource management, intellectual property management, supply chain management, operations management, and marketing, among others. It can be helpful to view the business plan as a collection of sub-plans, one for each of the main business disciplines.
"... a good business plan can help to make a good business credible, understandable, and attractive to someone who is unfamiliar with the business. Writing a good business plan can’t guarantee success, but it can go a long way toward reducing the odds of failure."
Traditionally business plans have been highly confidential and quite limited in audience. The business plan itself is generally regarded as secret. However the emergence of free software and open source has opened the model and made the notion of an open business plan possible.
An open business plan is a business plan with unlimited audience. The business plan is typically web published and made available to all.
In the free software and open source business model, trade secrets, copyright and patents can no longer be used as effective locking mechanisms to provide sustainable advantages to a particular business and therefore a secret business plan is less relevant in those models.
While the origin of the open business plan model is in the free software and Libre services arena, the concept is likely applicable to other domains.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
